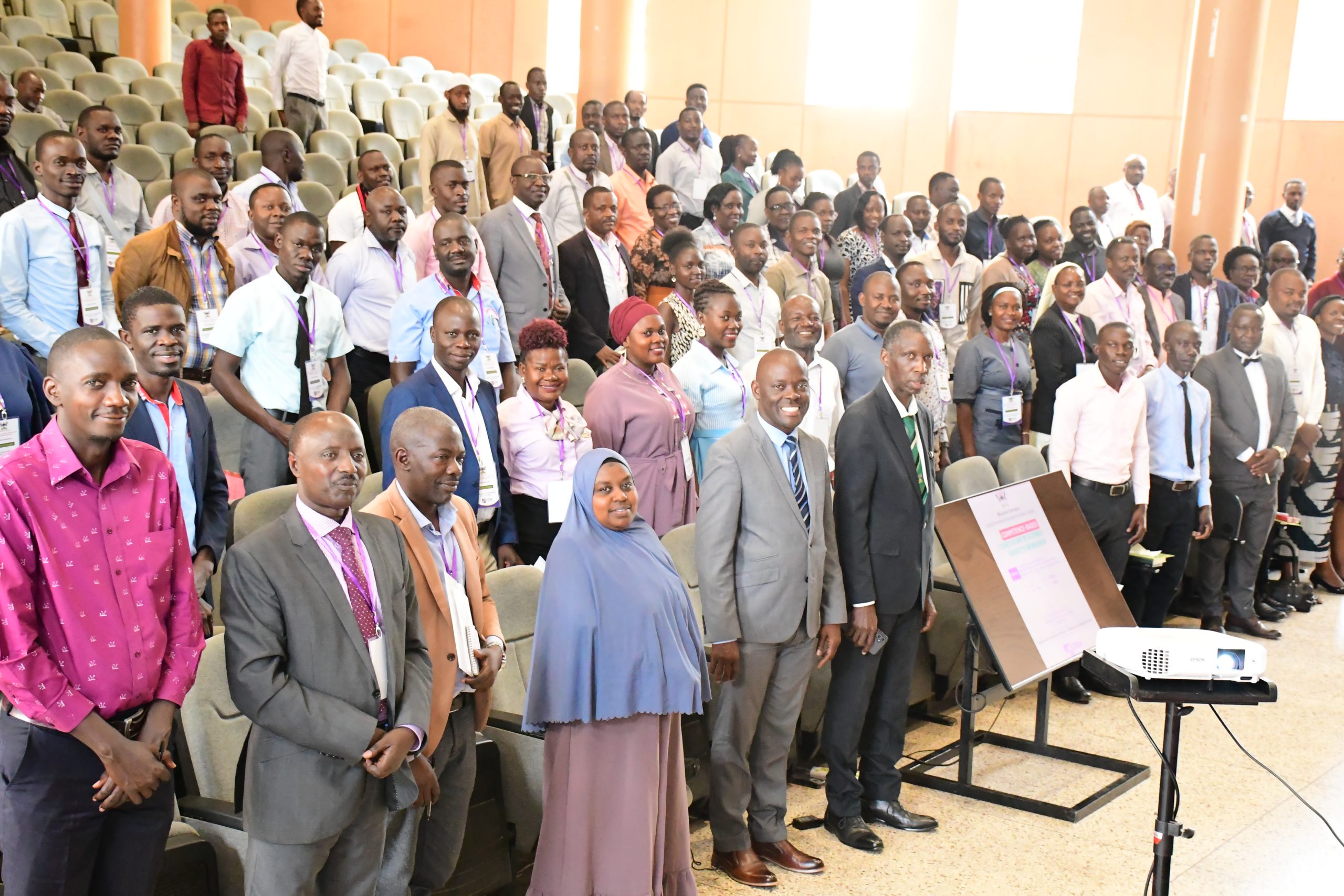
Makerere University’s College of Education and External Studies (CEES), through its Department of Science, Technology, and Vocational Education (DSTVE), on Friday 18th July 2025, hosted a high-level workshop for secondary school administrators focused on the implementation and assessment of the Competency-Based Curriculum (CBC) in science subjects.
The day-long workshop, held under the theme “The Role of School Administrators in Implementing and Assessing the Competency-Based Curriculum for ‘O’ and ‘A’ Levels of Secondary Schools,” drew participants from across Uganda’s secondary school education sector — head teachers, directors of studies, and other senior school leaders charged with ensuring that Uganda’s schools align with the country’s evolving education goals.
The workshop, held at Makerere University Yusuf Lule Central Teaching Facility Auditorium, was not just a dialogue but a clarion call to administrators to take ownership of their critical role in transforming science education through effective leadership, monitoring, and support for their teachers.
Addressing the Gap Between Policy and Practice

In her remarks, Dr. Marjorie S. K. Batiibwe, Head of DSTVE at Makerere University, welcomed participants and underscored the unique responsibility of administrators in ensuring the success of the competency-based reforms. “Teachers may have the necessary qualifications — some even hold master’s degrees — but without your support as administrators, the implementation of CBC risks remaining theoretical,” she said.
Dr. Batiibwe highlighted the Department’s long-standing contribution to teacher training in sciences — Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Mathematics, Agriculture, Food and Nutrition — and stressed the department’s commitment to building the capacity of educators at all levels. “We train both undergraduate and postgraduate teachers. We recognize that without a supportive school environment led by informed administrators, even the best-trained teachers will struggle to implement CBC effectively.”
She also pointed out persistent challenges, including low female participation in science subjects, reaffirming the department’s commitment to programs that encourage girls’ engagement in STEM through mentorship, science expos/exhibitions, and career guidance initiatives.
The Critical Role of Mindset Change
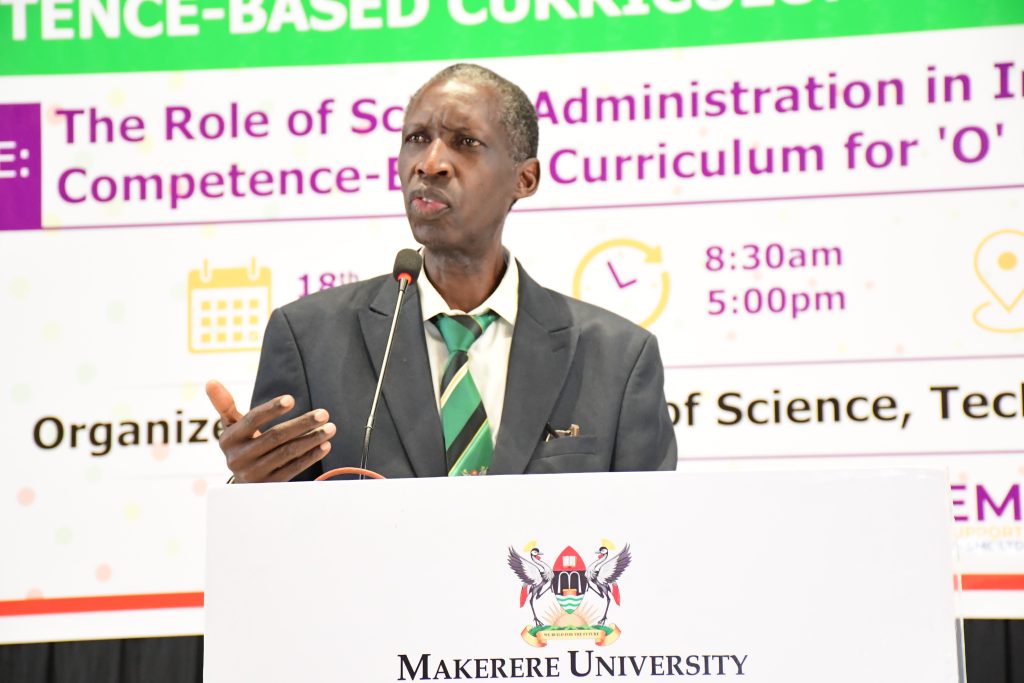

Delivering the keynote address, Prof. Anthony Muwagga Mugagga, Principal of CEES, spoke candidly about Uganda’s education history and the entrenched attitudes that continue to undermine progress. Drawing from his personal journey —which demonstrated that he struggled as a science student throughout his academic journey leading to a professor of philosophy — Prof. Mugagga stressed that Uganda’s greatest challenge is not lack of intelligence, but a failure to cultivate the right mindset among both educators and learners.
“What fails our students is not intelligence, but mindset. Every student is capable; it’s the teacher and the school leader who either unlocks or blocks that potential,” Prof. Mugagga remarked. He challenged school leaders to champion a shift in attitudes, especially among teachers who may still be clinging to outdated, exam-focused methods.
He illustrated this with a moving anecdote about his own daughter, who failed Senior 4 on her first attempt, but succeeded spectacularly after being allowed to choose subjects she was passionate about. “Mindset change — in both the student and the teachers — was what made the difference,” he said.
Science Education Must Translate into Practical Competence
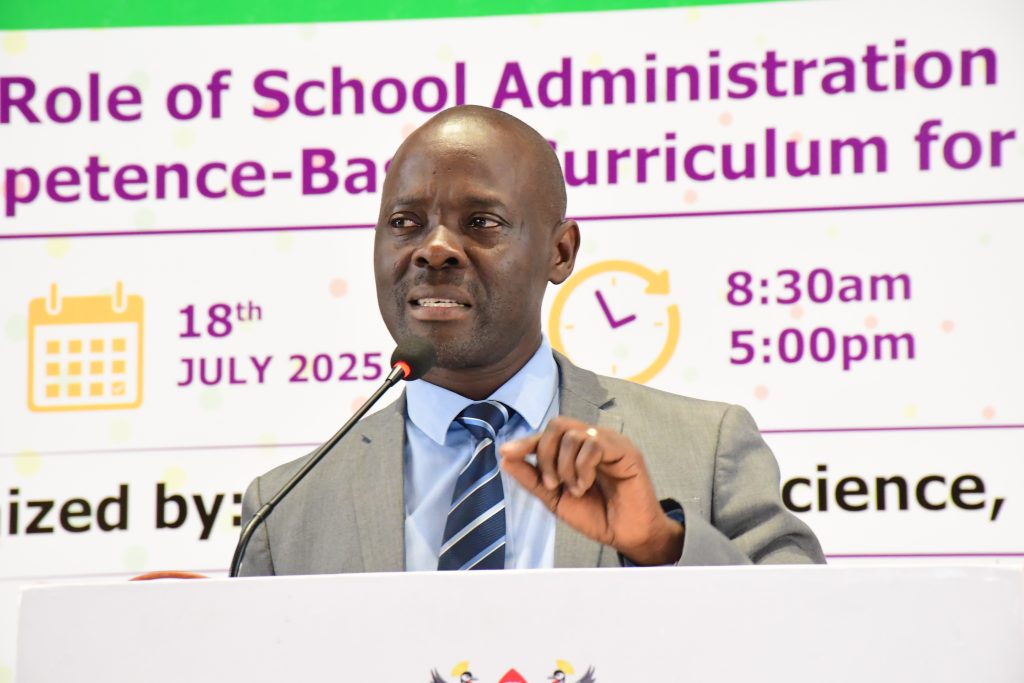

Associate Professor Mathias Mulumba Bwanika, Dean of the School of Education, framed his remarks around the practical implications of science education for Uganda’s transformation agenda. He highlighted that Uganda’s heavy investment in STEM disciplines comes with expectations. “Science teachers are not just preparing students for exams, but for life,” he said.
Using the example of China’s pragmatic approach to education, Associate Prof. Mulumba lamented Uganda’s culture of theoretical science instruction. “If your physics or biology student cannot fix simple problems at home, we are failing. Science must be practical,” he emphasized.
He called on administrators to establish structures within their schools for continuous professional development, arguing that successful CBC implementation requires ongoing learning, collaboration, and leadership from school management. “The curriculum is only as good as its implementation. Administrators must lead from the front,” he urged.
Teachers Struggling Between Old Habits and New Demands
Mr. Mudde Moses Ronald, a national trainer under SESEMAT at the Ministry of Education and Sports, painted a realistic picture of the challenges teachers face transitioning from knowledge-based to competency-based approaches. “Many teachers are caught between what they were taught and what is now expected. They are not resistant out of defiance, but because they are confused or not supported,” he said.
Mr. Mudde emphasized the importance of problem-based learning in CBC, where learners are encouraged to identify real-life challenges and devise solutions. He gave an example of learners tackling environmental degradation through problem identification, questioning, and solution generation — a model he said fosters critical thinking and application of science to everyday problems.
He acknowledged persistent gaps: “Some teachers still struggle with asking the right questions, with lesson planning, or even with technology. Administrators must create environments that support rather than punish these efforts.”
He called for continuous training, peer mentorship, and supportive leadership to help teachers adapt and thrive under CBC.
NCDC: The Curriculum is Sound, But Schools Must Act

Mr. Wilson Ssabavuma from the National Curriculum Development Centre (NCDC) offered a comprehensive overview of Uganda’s CBC reforms and reiterated the government’s commitment to providing resources and training. He traced Uganda’s curriculum reform journey, rooted in the need to move away from colonial models towards education that fosters problem-solving, creativity, and socio-economic transformation.
“Education must help learners transform themselves and their communities. Otherwise, we are wasting time,” Mr. Ssabavuma said. He explained that Uganda’s CBC emphasizes practical activities, continuous assessment, and learner-centered methods over rote memorization.
He acknowledged implementation challenges — from resource gaps to teacher resistance — but warned against passivity. “Schools and teachers must stop waiting passively. Take initiative. Engage with professional learning communities, peer coaching, and in-house training. The curriculum is there; success depends on how well you implement it,” he advised.
The Way Forward: Administrators as Change Leaders
Throughout the day’s discussions, a consistent message emerged: school administrators are not passive observers, but active leaders in the CBC journey. Their role is to ensure that teachers are equipped, supported, and monitored effectively. This includes embracing policies such as the Continuous Professional Development (CPD) requirement of two hours per week, fostering internal collaboration, and aligning school objectives with national education goals.
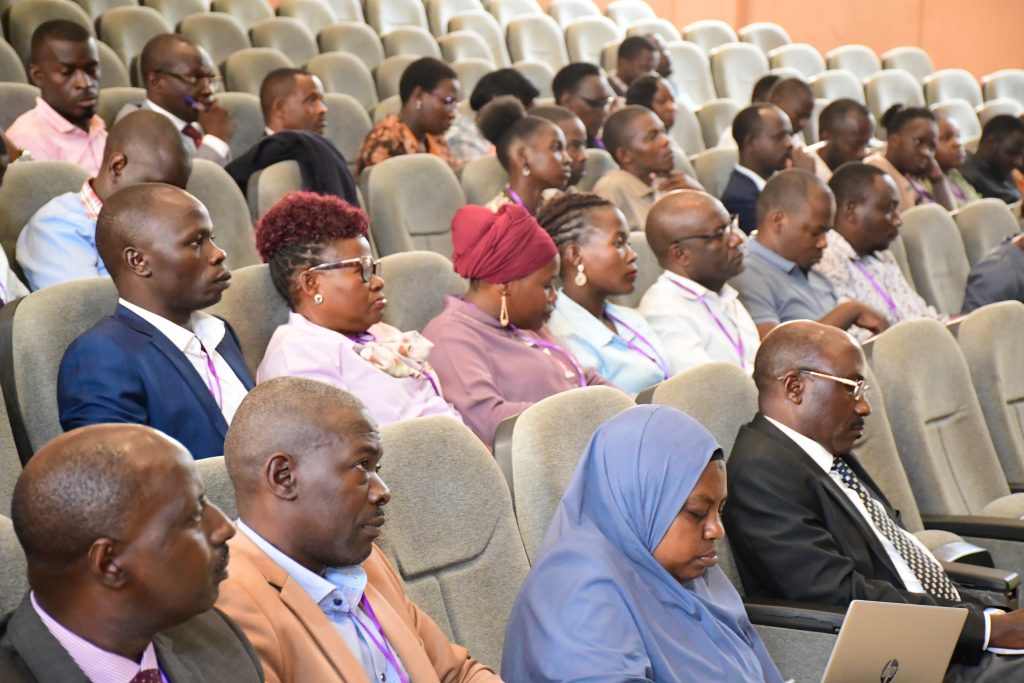

Administrators were reminded that effective leadership in CBC implementation requires more than enforcement — it demands understanding, empathy, and strategic support for teachers grappling with the transition. The workshop emphasized that the success of Uganda’s competency-based reforms hinges on school leaders modeling the very competencies they seek to instill: critical thinking, adaptability, collaboration, and innovation.
Conclusion: A Collective Responsibility for Uganda’s Future
As the workshop drew to a close, participants left with a renewed sense of purpose. They were challenged to return to their schools not just as managers, but as champions of a transformative vision for science education — one where every learner is equipped to solve real-world problems, contribute meaningfully to society, and drive Uganda’s socio-economic development.
Dr. Batiibwe captured the spirit of the day in her closing remarks: “Let us stay connected, let us share experiences, and let us continue working together for the good of our learners, our schools, and our country.”
The success of CBC, it was made clear, will depend not just on policies or curricula, but on the daily decisions, attitudes, and actions of school leaders across Uganda.




